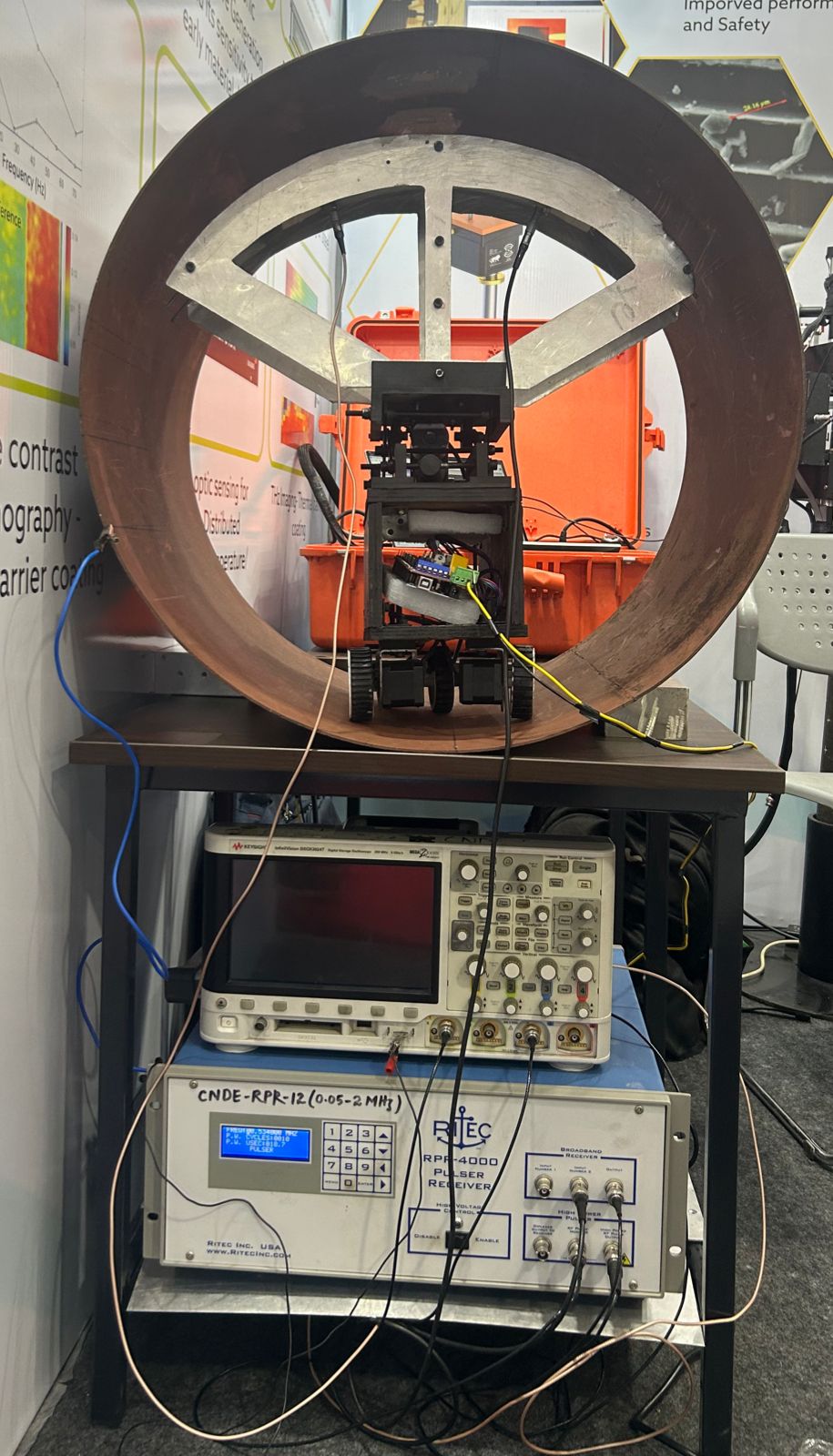
Industrial pipeline systems are commonly used to transport oil, gas and petrochemical products. In-service inspection is required to avoid catastrophic failures and to guarantee the safe operation of pipelines.
Testing large structures using conventional bulk ultrasonic wave techniques is slow because the test region is limited to the area immediately surrounding the transducer. Therefore, scanning is required if the entire structure is to be tested.
Also, A high proportion of these industrial pipelines is insulated, so that even external defects cannot readily be detected without the removal of the insulation which in most cases is prohibitively expensive. There is therefore a need for the development of a quick, reliable method for the detection of defect under insulation.
This study aims to investigate the propagation characteristics of Shear Horizontal (SH) ultrasonic guided waves in steel pipes using Electromagnetic Acoustic Transducer (EMAT) technology, with a specific focus on weld defect and pipe wall remnant thickness.
During my MTech, i design experiments and set up EMAT systems to evaluate SH wave propagation, weld defects, and remnant thickness in steel pipes.
Conduct experiments, collect data, and analyze wave behavior under various conditions. Simulation & Validation: Use tools like Abaqus to simulate SH wave propagation and validate results against experiments.
Performance Evaluation: Assess the accuracy and reliability of EMAT-based SH wave techniques for real-world defect detection, including insulated pipes.